Inside: A complete guide to blue birds in Nebraska including a full-color photo of each blue bird, details about habitat, diet – including feeder food they’ll eat, appearance, nesting habits, and a range map to show you where in the state you can expect to see them.
You spotted a blue-colored bird in Nebraska. The next step is to identify it. I got you!
With more than 20 years of experience attracting backyard birds to my yard (Wisconsin), I’ve studied all of the blue-colored birds in my area so I have the information you’re looking for. For the remaining blue-colored bird species, I rely on my trusty sourcebooks and friends at The Cornell Lab of Ornithology to guide me.
I’ll never forget my first blue-colored bird spotting – which I later learned was an Indigo Bunting! You’d have thought I’d seen Elvis in my backyard. I screamed “blue bird, blue bird” and ran around my house like a lunatic looking for my camera. It was still there when I returned, but not for long. I looked him up in my guide book and there he was in all his royal blue glory. Breathtaking.
All Variations Of Blue Birds In Nebraska Are Included
This article includes blue-colored wild bird species in Nebraska that range in size from tiny & small to large. The bird could be all blue or partly blue with a secondary color. They could be bright blue birds, dark blue birds, or light blue birds – all variations are here!
Some blue-colored birds live in Nebraska year-round, others are here to breed, and others are migrating through. The range maps are color-coded so you know if it’s a year-round bird, there to breed, migrating through, or there during a nonbreeding time.
I also included a beautiful photo to help you identify these blue beauties along with detail such as:
- Size + appearance description
- Diet in the wild and at the feeder
- Habitat
- Nest & eggs description
- Range map
My hope is that this article will help you easily identify the blue bird you saw or plan to see one day. So let’s get at it, here are the blue-colored birds in Nebraska:
Blue-Colored Birds In Nebraska
Barn Swallow
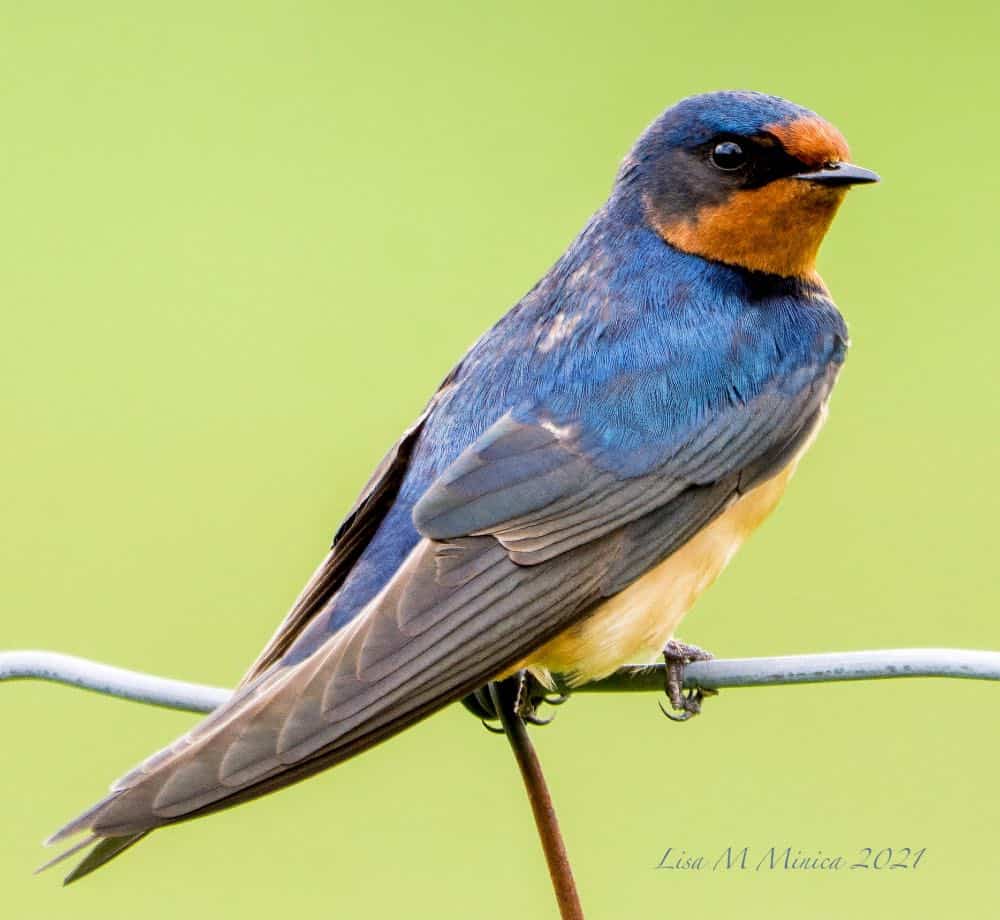

Appearance: 7″ long, steel blue glossy on top, chestnut forehead and throat, and rust-orange underparts. Long forked tail with a white base. The female’s coloring is lighter and the tail shorter.
Diet: Insects, preferably beetles, wasps, and flies. Drinks by skimming the surface of the water.
Feeder food: Not likely to visit a feeder.
Habitat: Open fields and pastures.
Nesting: A barn swallow typically nests in or on a manmade structure such as a barn. Builds nests of mud. 2 broods/season, 4-5 eggs per brood, eggs are white with brown markings, incubation from 13-17 days.
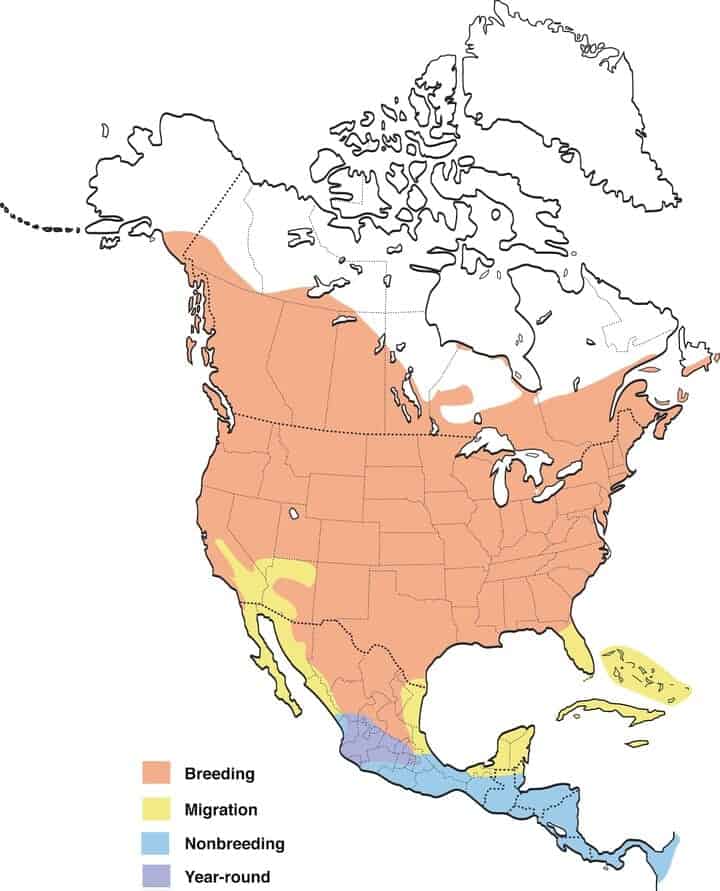
Migration: Barn swallows are migrators. In spring, they’ll migrate north into the US and Canada for breeding and to raise their young. When fall comes, they’ll head south to Mexico’s southern states. That said, they do maintain a year-round range in central Mexico where they remain for every season.
Range Map
Belted Kingfisher
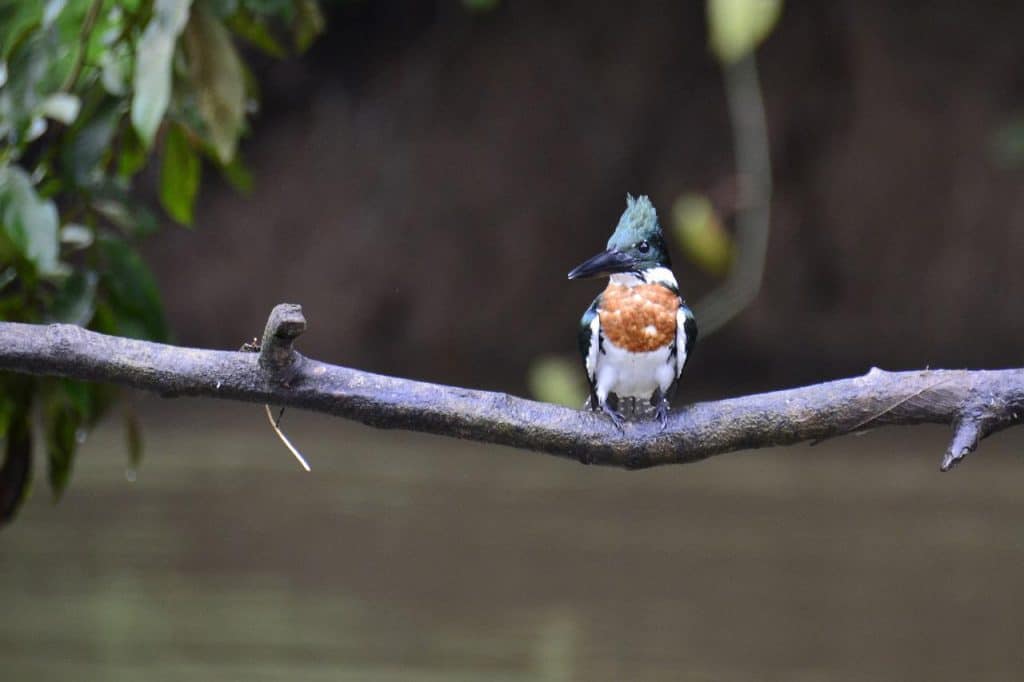

Appearance: The belted kingfisher is a large 13″ long bird with a large head, long bill, and stocky body. Blue/gray throughout with white ring around neck and white chest. The Female is the same but with an additional chestnut band on her chest.
Diet: Large 13″ long bird with a large head, long bill, and stocky body. Blue/gray throughout with white ring around neck and white chest. The Female is the same but with the additional chestnut band on the chest.
Feeder food: Unlikely to come to the feeder but often attracted to yards with streams or ponds.
Habitat: Near streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, and calm marine waters – especially unclouded water with little vegetation.
Nesting: Belted kingfishers dig burrows along the water’s edge for their nest. 1-2 broods/season, 5-8 eggs/brood – large white glossy eggs (1.5″ long), 22-24 days incubation.
Migration: Many but not all belted kingfishers are migrators. In spring, the migrators will head north into Montana, North Dakota, northern Minnesota, Canada, and Alaska to breed and raise their young. When fall comes the migrators head back south – as far south as Arizona, New Mexico, southern California, and Mexico.
Year-round range: All US states (except North Dakota and Arizona) and the pacific coast of Canada’s British Columbia.
Breeding range: While some stay in their year-round range, many others migrate north into Montana, North Dakota, northern Minnesota, Canada, and Alaska to breed and raise their young. When fall comes the migrators head back south – as far south as Arizona, New Mexico, and southern California.
Winter range: While many belted kingfishers migrate south for winter, just as many remain in their year-round range when the temperatures dip.
Range Map
Blue Grosbeak
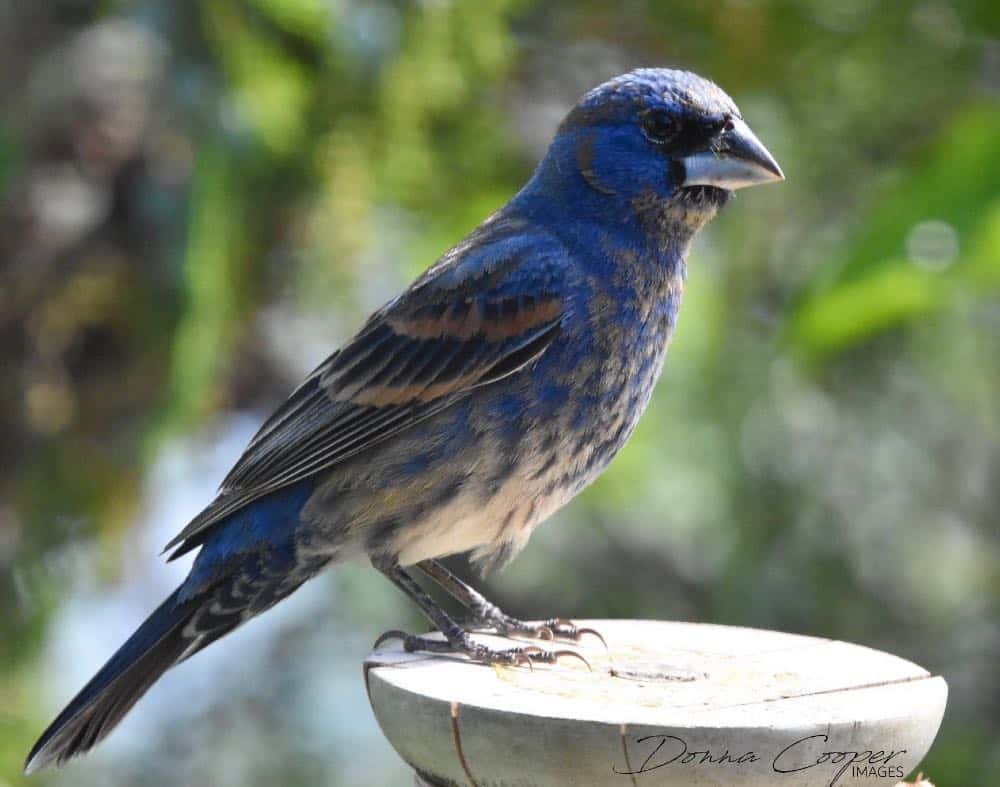

Appearance: Blue grosbeaks are medium birds about 8″ long, large, bright blue, with large silver bills, and chestnut wingbars. The female’s primary color is light cinnamon with darker-colored wings.
Diet: Insects, seeds, and grains.
Feeder food: Grain and birdseed.
Habitat: Thick shrubbery and areas with tall trees.
Nesting:
- Nest: Small cup-shaped nest of twigs and miscellaneous organic materials resting in low-lying trees, shrubs, and bushes.
- Brood: 1-2 broods/season
- Clutch: 3-5 eggs/brood
- Egg color: Pale blue to white with occasional brown spots
- Egg size: 0.8 inches by 0.7 inches
- Incubation: 12-13 days incubation.
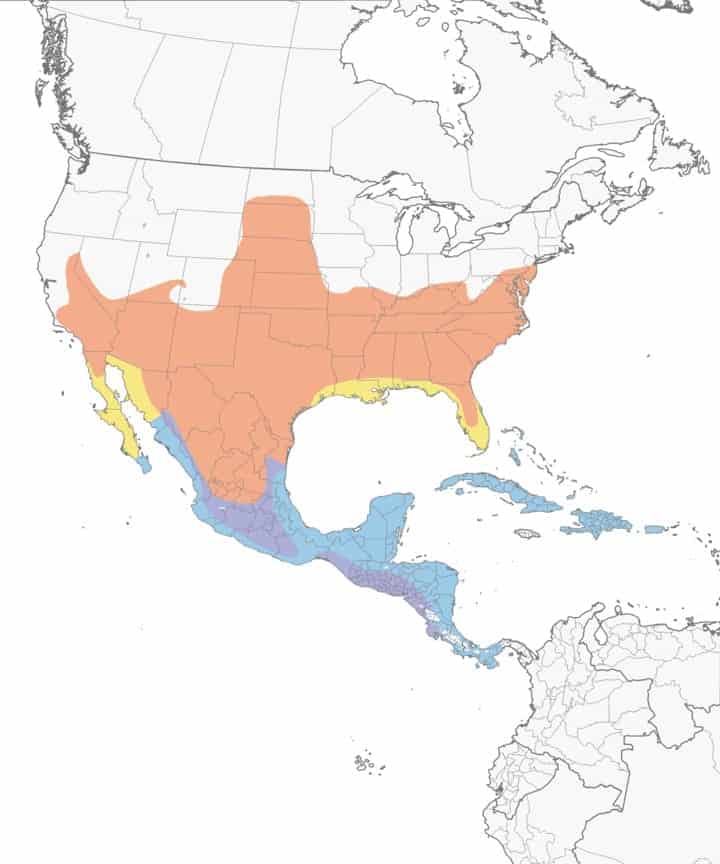
Migration: Blue grosbeaks are migrators. In spring, they migrate north into the US to breed and raise their young. Then in the fall, they head back south for the winter. There is a small area in Mexico they call their year-round home. The birds in this area don’t typically migrate.
Year-round range: Parts of Mexico.
Breeding range: Southern half of the US as well as North Dakota, South Dakota, and Kansas.
Winter range: Mexico and the Caribbean islands.
Range Map
Blue Jay
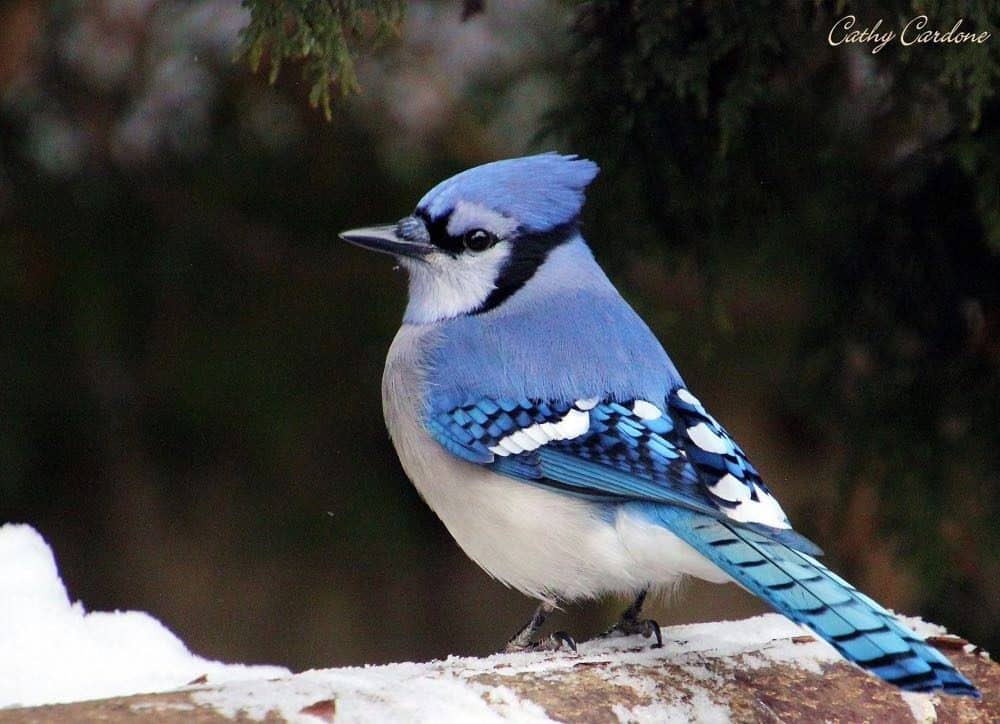

Appearance: Large bird 12″ long, medium blue & white body, blue crest (which he flattens at will), gray belly, and white face. White & blue wings with black spots. Females look the same.
Diet: Insects, fruit, seeds, nuts, other birds’ eggs, and nestlings.
Feeder food: Whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, and cracked corn.
Habitat: Forested areas with mixed tree types. Also common in suburbs and urban areas.
Nesting:
- Nest: bulky large nest made from twigs, bark, and mud resting on a tree branch about 5-50′ up.
- Broods: 1-2 broods/season,
- Clutch: 2-7 eggs/brood,
- Egg color: Pale blue to a light brown base color, and these eggs usually have brown or gray spots.
- Egg size: 1 inch by just under 1 inch
- Incubation: Both parents incubate the eggs for 17-18 days and the young fledge between 17-21 days.
Migration: In general, blue jays are not migrators. They remain in their year-round range for all 4 seasons – even during the breeding season. While they may move within their year-round range, they do not regularly head north for breeding and south for winter as some species do. That said, in rare cases, some will head west of their year-round range for the winter.
Range Map
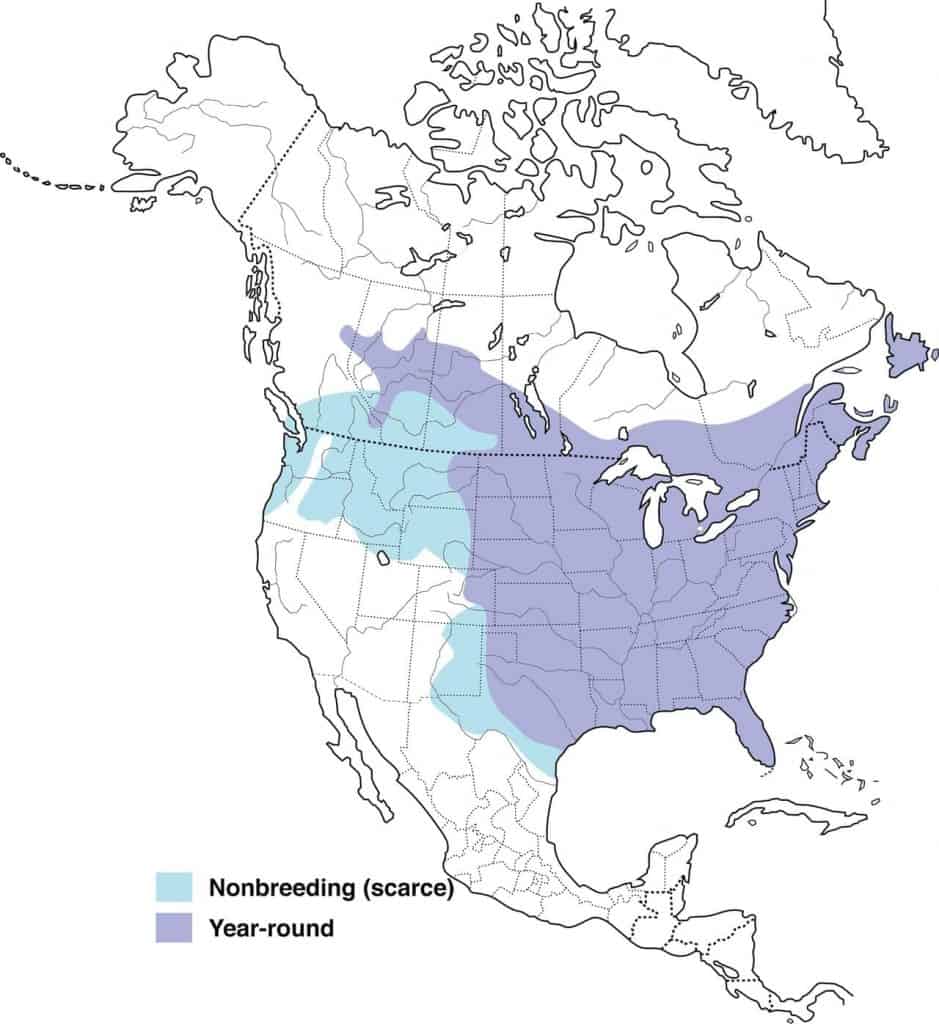
Blue-Gray Gnatcatcher
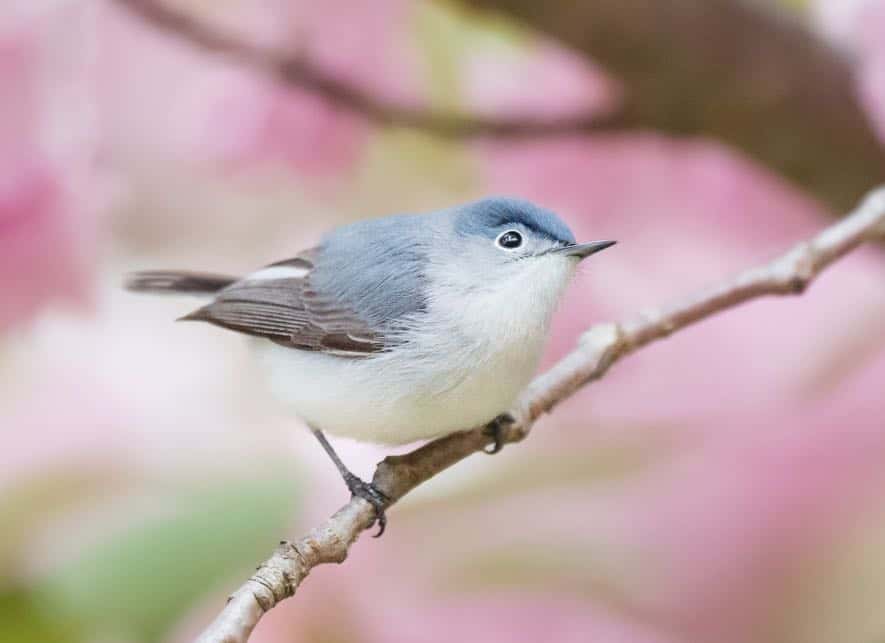

Appearance: Blue-gray gnatcatchers are tiny birds 4.25″ long, with soft blue/gray upperparts, white eye-rings, white underparts, and long black long tails with white under. The females are the same. The breeding male is accented with narrow black eyebrows.
Diet: Insects and spiders.
Feeder food: Unlikely to visit the feeder.
Habitat: Deciduous forested areas.
Nesting:
- Nest: Tidy cup-shaped nest of natural fibers, bark, and spiderweb about 3-80′ high in a tree or shrub.
- Broods: 1-2 broods/season
- Clutch: 3-5 eggs/brood
- Egg color: Pale blue with red/brown spots.
- Egg size: 0.5 – 0.6 inches by 0.4 – 0.5 inches
- Incubation: 11-15 days and the young fledge at about 10-15 days.
Migration: While many blue-gray gnatcatchers remain in their year-round range during the spring & summer, most migrate north into the US for breeding and to raise their young. The migrators then head back south in the fall and return to their year-round range or even further south along the Mexican Pacific coast, southern Florida, and the Caribbean islands to spend winter.
Year-round range: The southernmost part of these US states: California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Louisiana, Georgia, Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia.
Breeding range: Eastern half of the US as well as California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas, Kansa, and Oklahoma.
Winter range: Southern California, southwest Arizona, along the Pacific coast of Mexico, the southernmost tip of Florida, and the Caribbean islands.
Range Map
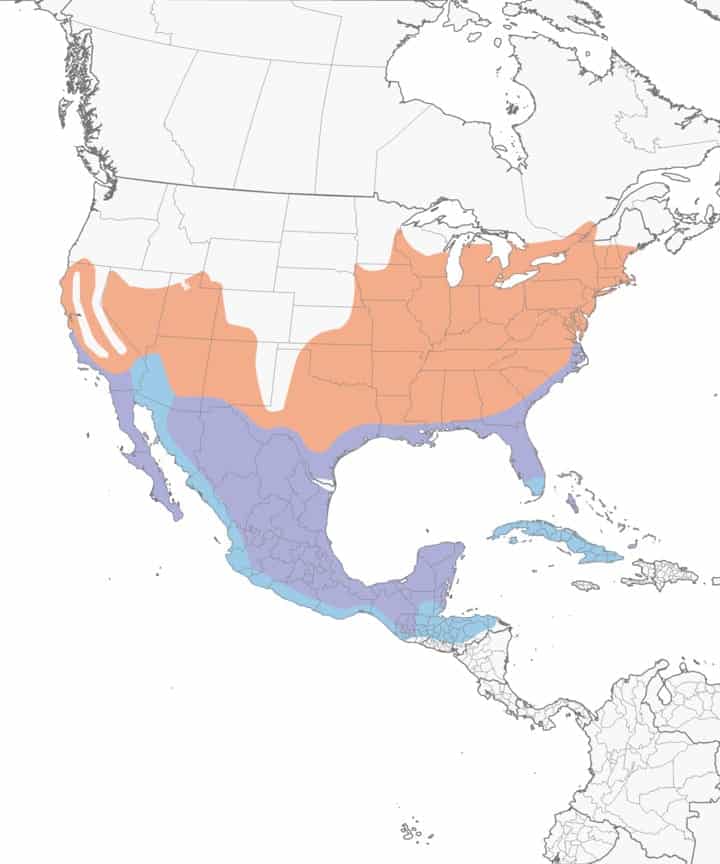
Common Grackle
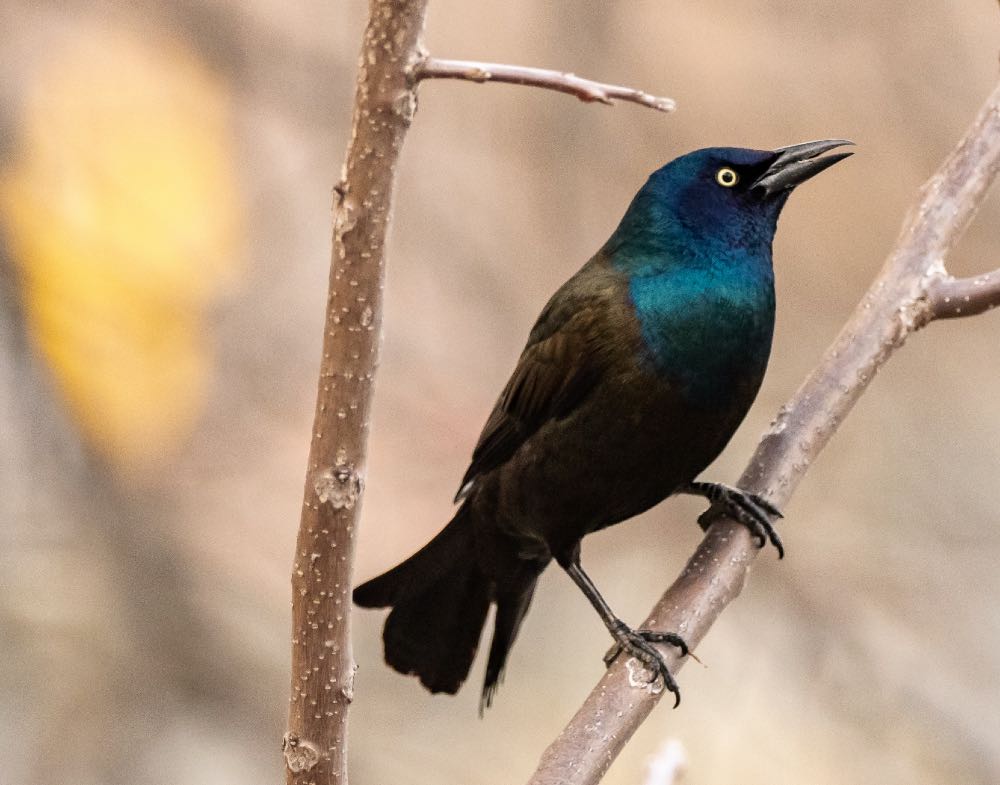

Appearance: The common grackle is a large bird about 12.5″ long bird with iridescent blue purple and bronze. Their eyes are yellow and they have long flared tails. The female is similar with less vibrant coloring (browner) and a shorter tail.
Diet: Insects, grains, seeds, fruit, scavenged garbage.
Feeder food: Sunflower seeds, black-oil sunflower seeds.
Habitat: Fields with scattered trees, open woodlands, farmlands, and marshes. Common in suburban yards.
Nesting: Bulky cup-shaped nest of twigs placed 3-20′ high in a conifer tree. 3-5 eggs incubated for 12-15 days. Young fledge at about 12-15 days.
Migration: Common grackles are migrators. While many remain in their year-round range all four seasons, many head north in spring (as far north as Canada’s Northwest Territories) to breed and raise their young. Then in the fall, they head back south into their year-round range. A small part of the population pushes further southwest of Texas.
Year-round range: Nebraska and the US states south and east of it. US states
Breeding range: Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, Kansas, western Kansas, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, the New England states, and all Canadian provinces (except for Nunavut and barely British Columbia).
Winter range: Southwest edge of their Texas year-round range.
Range Map
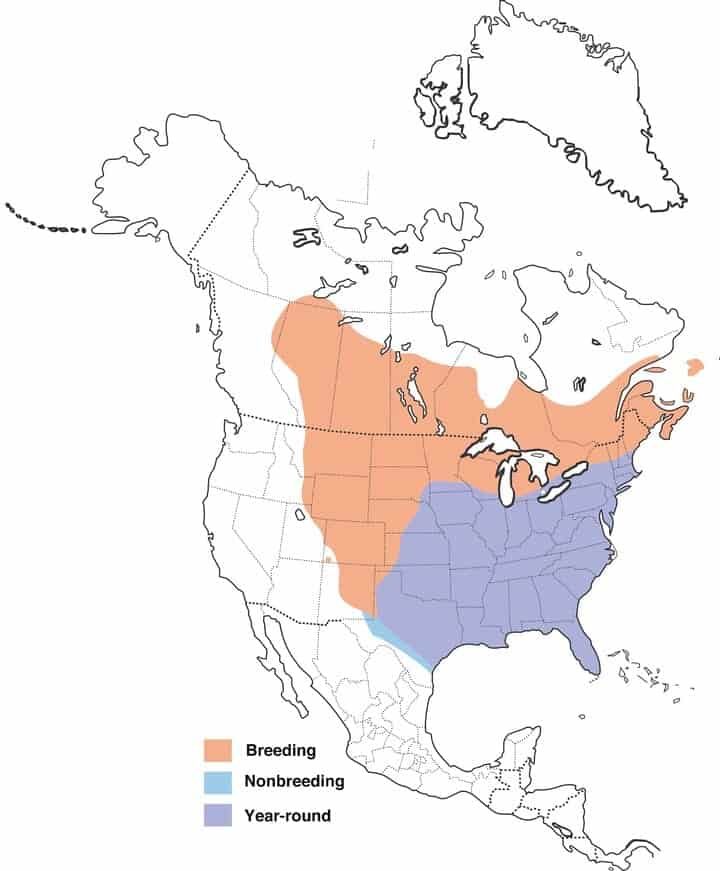
Eastern Bluebird
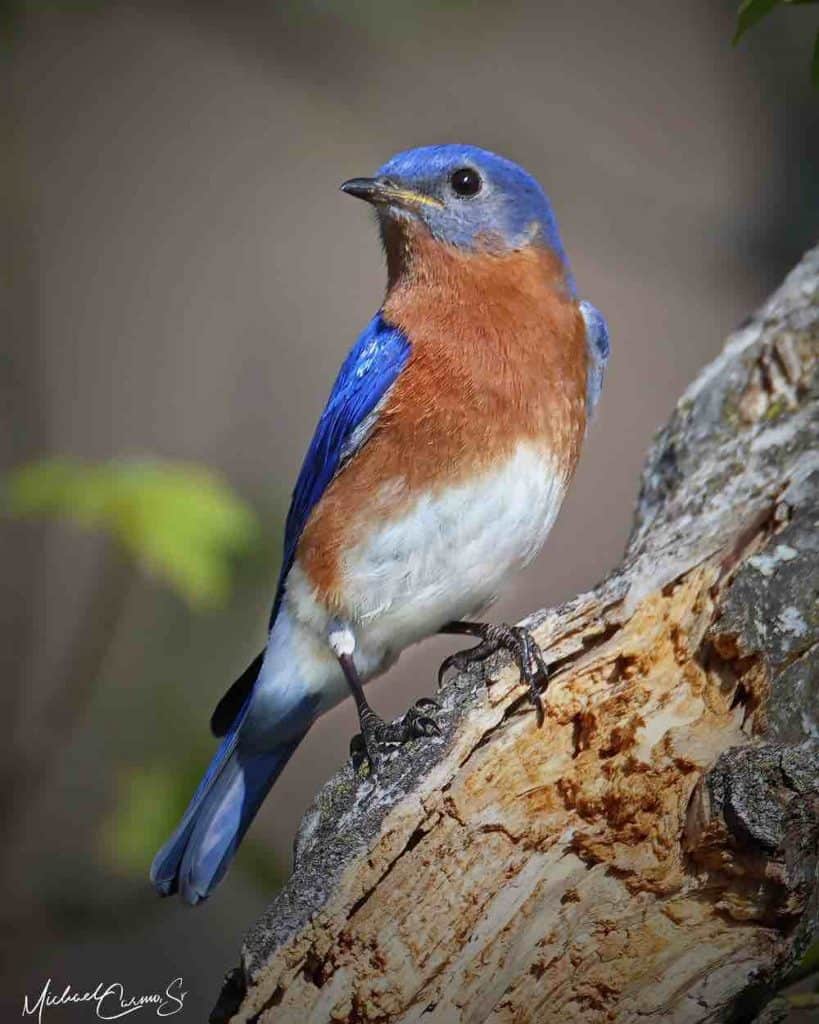

Appearance: Eastern bluebirds are small birds about 7″ long, royal blue, orange throat & breast, white belly & undertail. Female is similar but with more muted colors
Diet: Insects & spiders in spring/summer. Small fruit in Fall/Winter.
Feeder food: Suet, sunflower seeds, dried fruit, jelly.
Habitat: Wide-open spaces, fields, meadows.
Nesting:
- Nest: Cavity nesters. The male bluebird determines the nest site (an old woodpecker hole in a tree or manmade nestbox), but the female is the one who builds the nest. She keeps the nest for multiple broods.
- Brood: 2-7 broods/season
- Clutch: 4-5 eggs/brood
- Egg color: Pale blue eggs (sometimes white) with no blemishes or discoloration.
- Egg size: 0.9 inches by 0.8 inches
- Incubation: 11-19 days
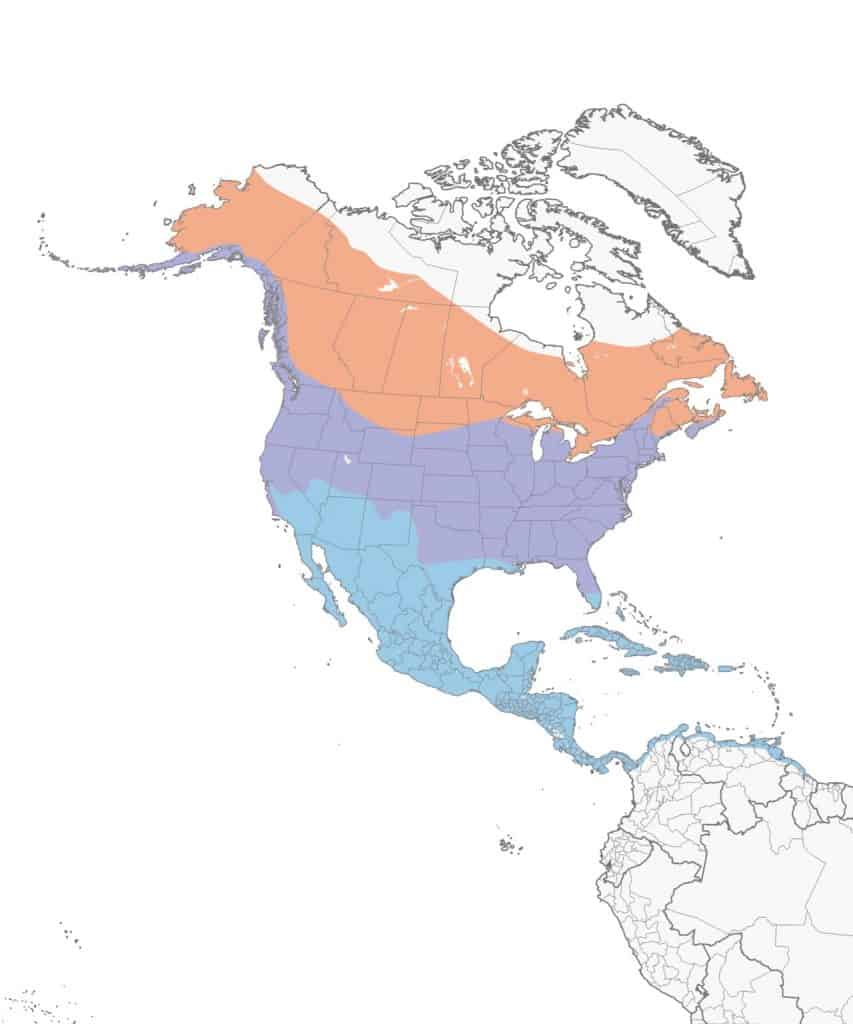
Migration: Some eastern bluebirds are migrators. While many remain in their year-round range all year long, some migrate north for breeding and raising their young then head south in winter back into the year-round range or further west into Colorado, New Mexico, and western Texas.
Year-round range: The US states south and east of Nebraska, Mexico, and Central America.
Breeding range: Northwest Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota, Minnesota, the northern half of Wisconsin & Michigan, New Hampshire, Maine, and the southern part of these Canadian provinces: Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
Winter range: Eastern Colorado, New Mexico, western Texas, and northeast Mexico.
Range Map
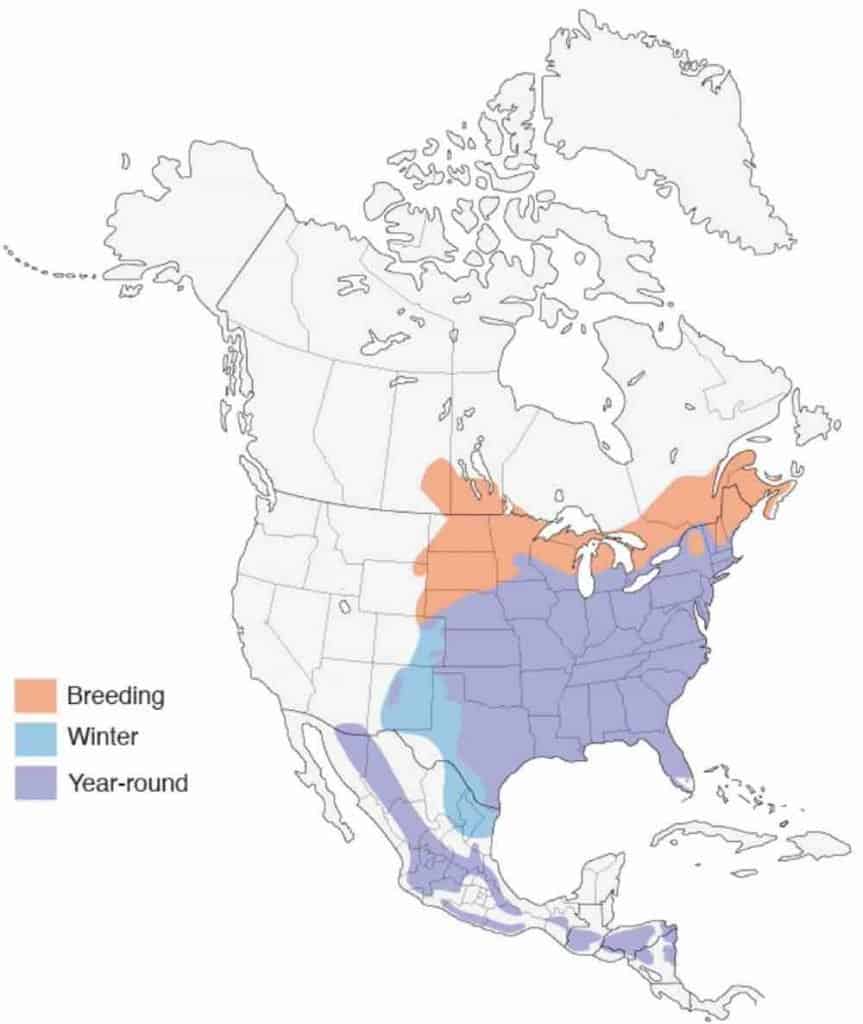
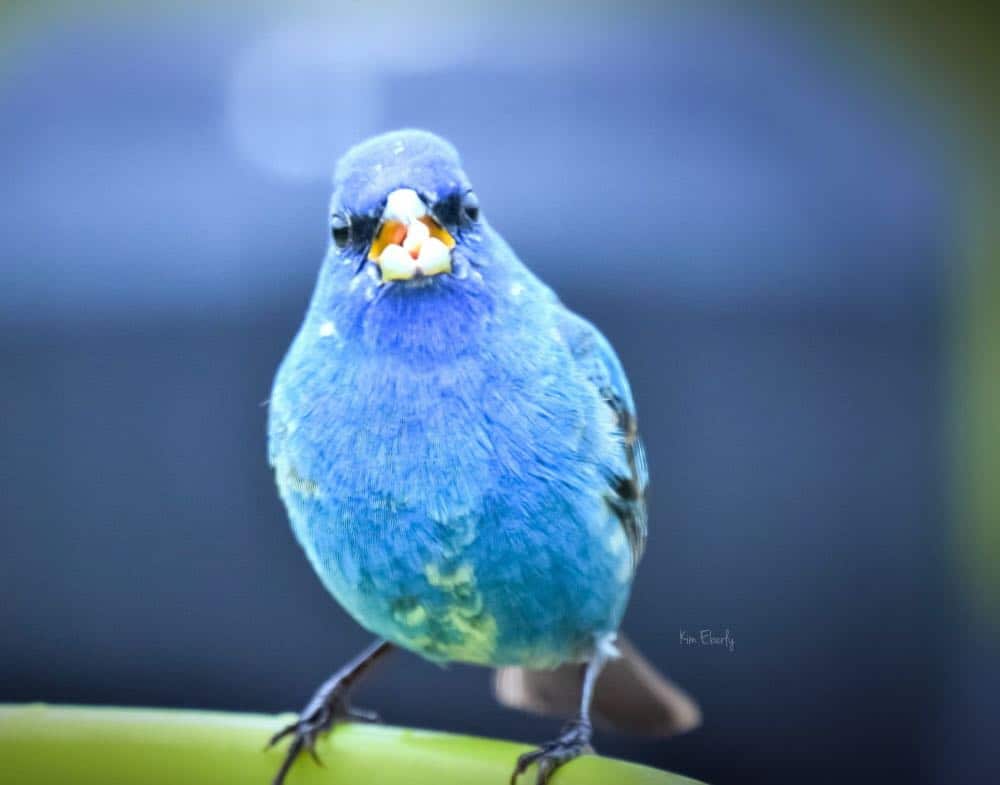
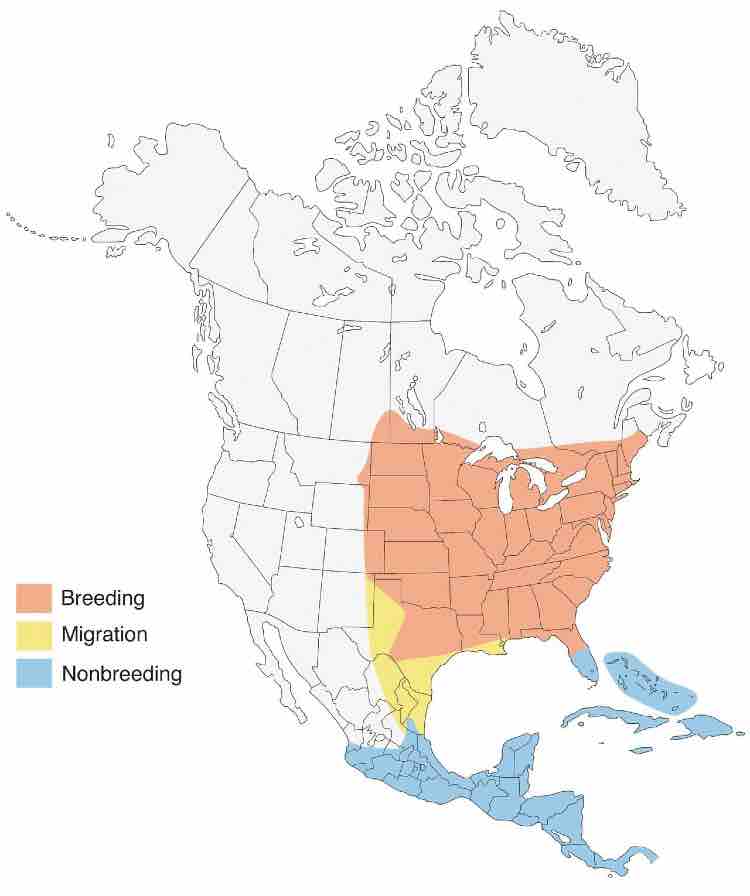
Indigo Bunting
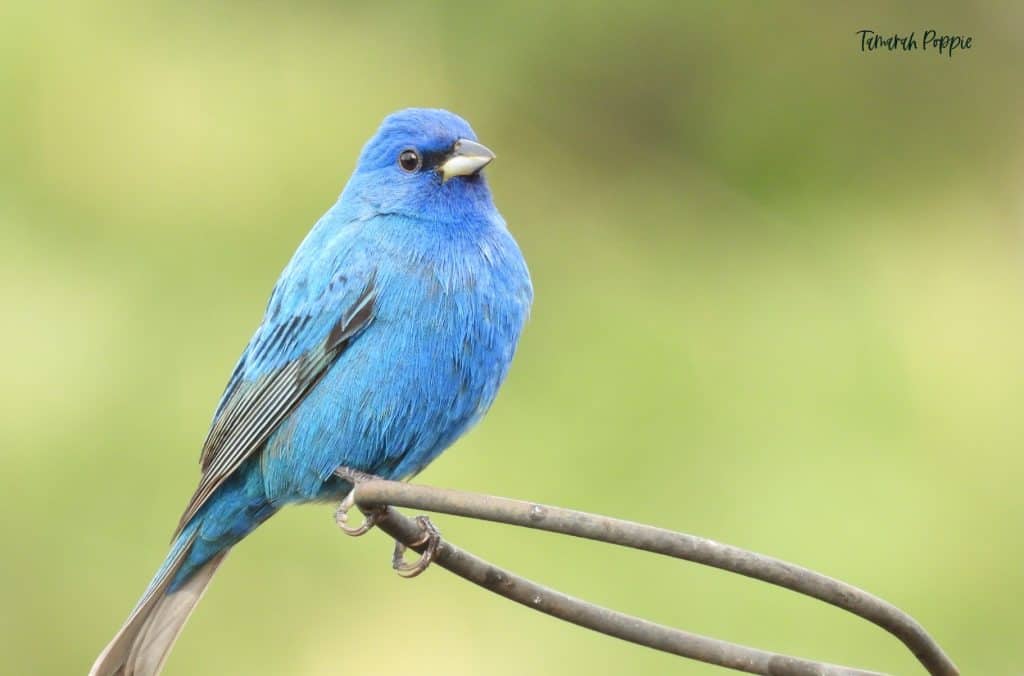

Appearance: Brushy fields, on weedy plants, scrub, and along the edges of the woods. Also in clearings within deciduous woods and edges of swamps.
Diet: Small seeds, insects, and fruits.
Feeder Food: Although not a regular at the feeder you may entice them with nyjer/thistle and white millet seeds.
Habitat: Brushy fields, on weedy plants, scrub, and along the edges of the woods. Also in clearings within deciduous woods, and edges of swamps.
Nesting: Cup-shaped nest in shrubs or trees 3′ high. Shrubs or trees 3′ high. 1-3 broods/season, 3-4 eggs/brood, eggs are white with few brown spots.
Range Map
For more detail about the Indigo Bunting such as its mating & nesting, how to attract them to your yard, and more: check out Proven Ways to Attract Indigo Buntings.
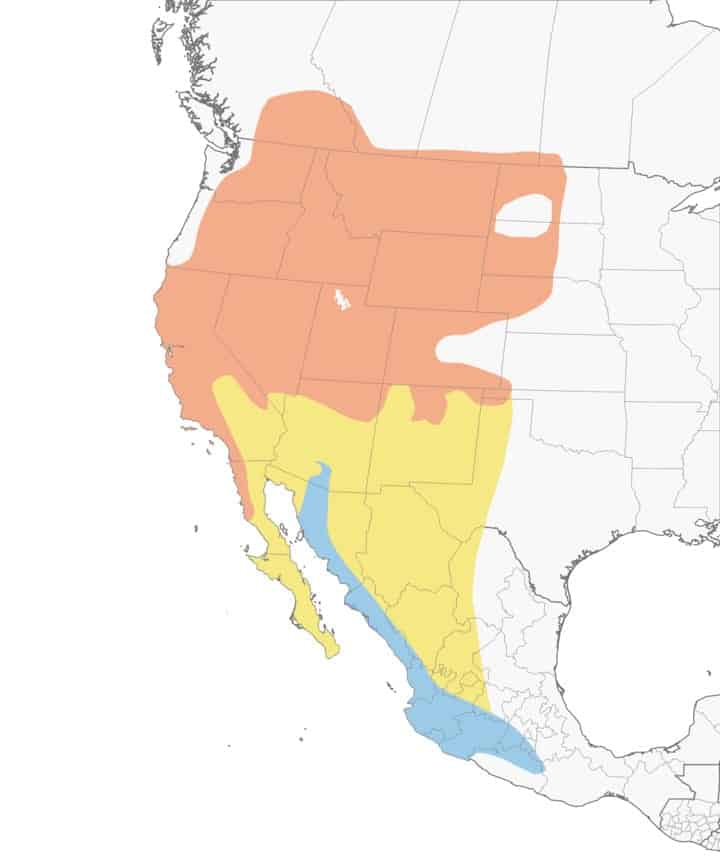
Lazuli Bunting
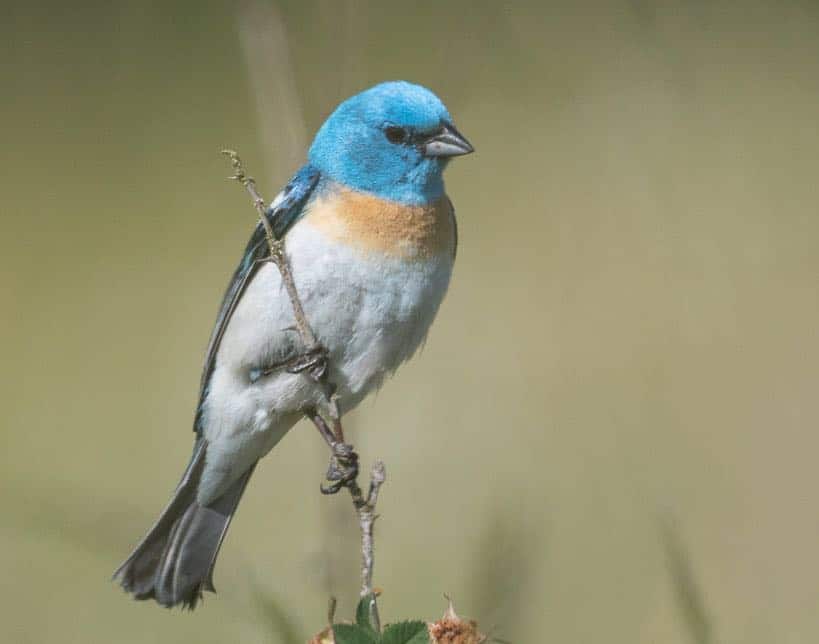

Appearance: Small bird 5-6″ long, brilliant blue on top, soft orange-cinnamon color chest, white belly and patch on the shoulder, cone-shaped bill, and slightly flat forehead.
Diet: Insects, fruits, and grasses.
Feeder Food: White proso millet, sunflower seeds, or nyjer thistle seeds.
Habitat: Open woodlands, brushy hillsides, thickets, and backyards throughout the West.
Nesting: Cup-shaped nest of bark, twigs, and leaves nestled in a shrub about 3′ up. They have 1-2 broods/season, 3-4 eggs/brood, and eggs are .7-.8″ long and pale blue to faint green/blue or white. 11-14 days incubation period.
Range Map
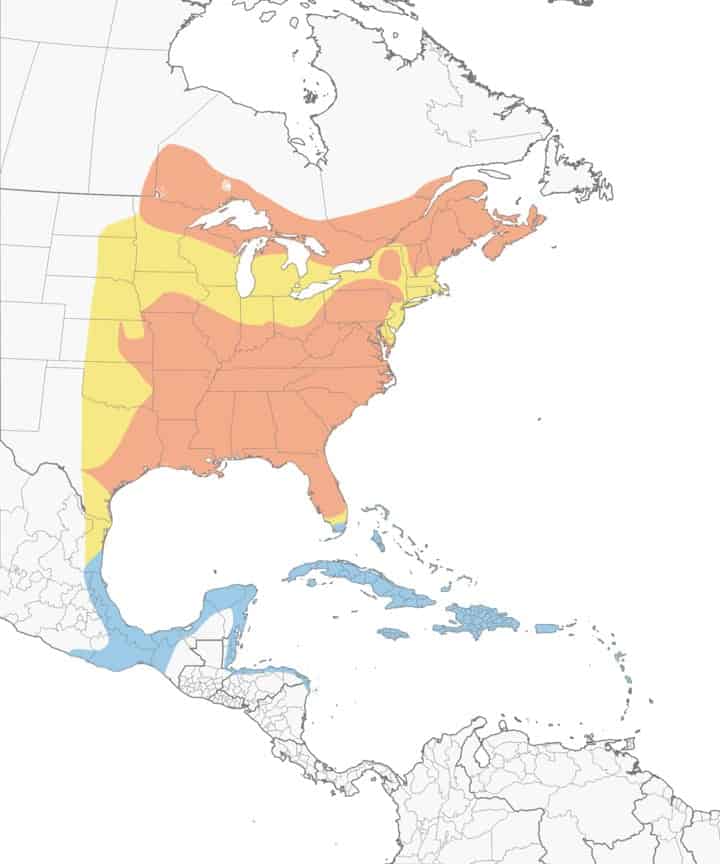
Northern Parula
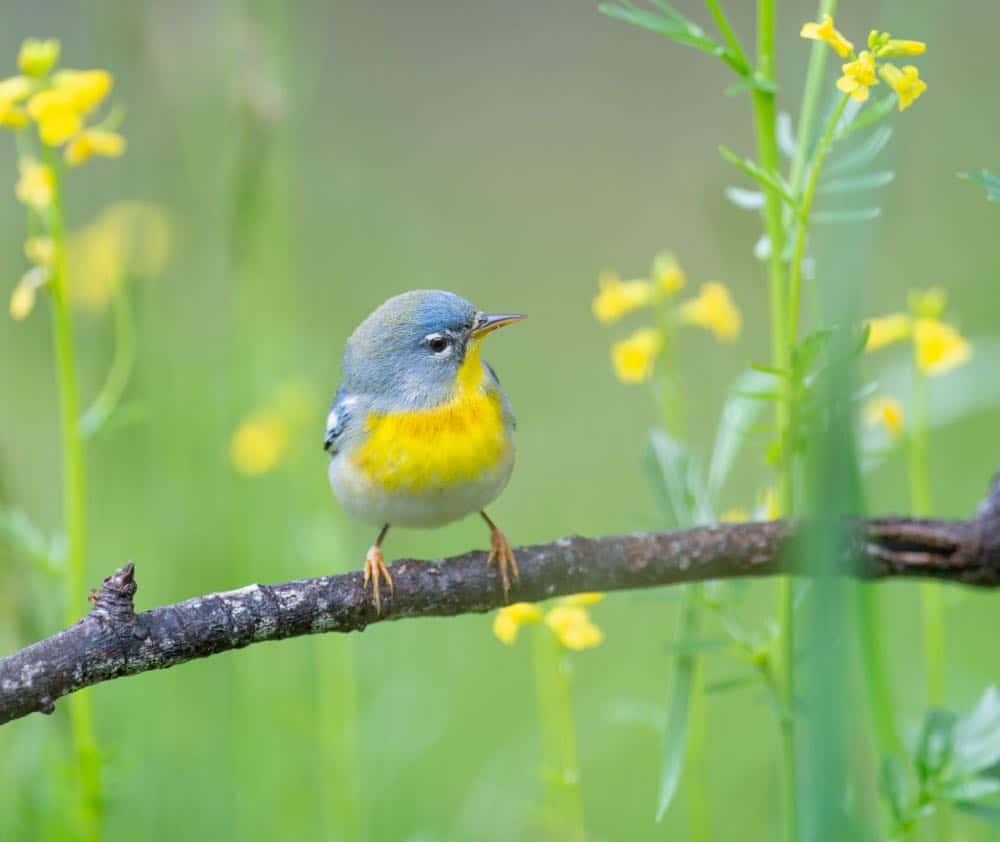

Appearance: Northern parula is a small bird about 4.5″ long, blue/gray with a yellow throat and back patch, bluish-gray overall with a yellow-green patch on the back, a brown band on the lower, and white strips above and below each eye. Females are similar but more muted colors. neck, and 2 white wing bars.
Diet: Spiders, insects, berries, seeds, nectar.
Feeder food: Unlikely to visit a feeder.
Habitat: Prefer forested areas especially when water is present (streams, marshes) and in the lowland where moss is present.
Nesting: Nests are built in mossy vegetation as high up as 100′ at the end of a branch. 1-2 broods/season, 2-7 eggs/brood, eggs are about .65″ long, white with red/brown/purple speckles, and incubation lasts about 12-14 days.
Migration: Northern parulas are migrators. In the spring, they migrate north to breed and raise their young. Then in the fall, they migrate south for the winter.
Breeding range: The US states south and east of Kansas, northern Minnesota, Wisconsin, & Michigan, Pennsylvania, New York, New England, and the southern parts of Canadian provinces Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec.
Winter range: Southern tip of Florida, the Caribbean islands, Mexico, and Central America.
Range Map
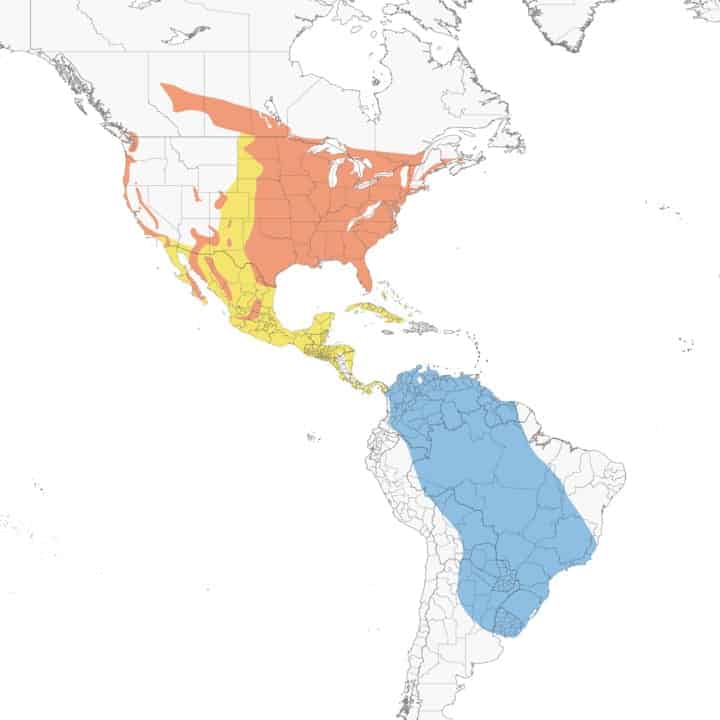
Purple Martin
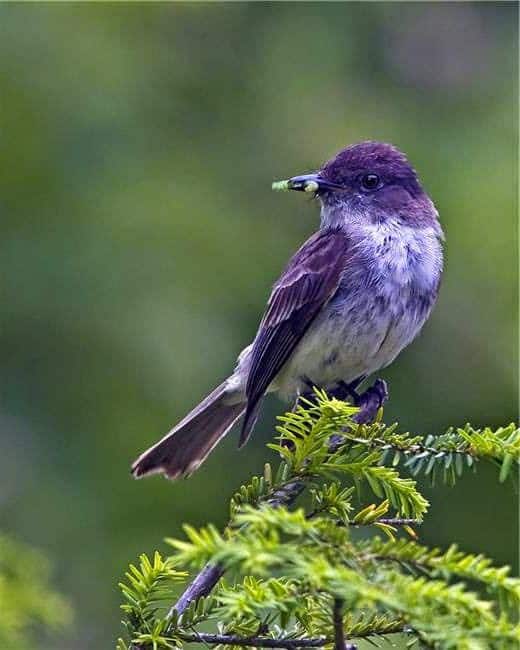

Appearance: The purple martin is a medium bird about 8.5″ long with a blue/purple head, back, and belly with black wings and tail.
Diet: Insects especially dragonflies.
Feeder food: Unlikely to visit a feeder.
Habitat: Usually within 100′ of human dwelling. Purple Martins exist in large colonies.
Nesting: Purple martins are cavity nesters. They primarily use manmade nest boxes which accommodate a colony of birds. They have 1 brood/season, 4-5 white eggs/brood, 15-18 days incubation, and fledge after 26-30 days.
Migration: Purple martins are migrators. They spend the winters in South America and migrate north to breed and raise young.
Breeding range: Pacific northwest coast of Washington, Oregon, and California, parts of Arizona, Utah, and Colorado, the eastern half of the US, and the southern parts of Canada’s Alberta, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Ontario.
Winter range: South America
Range Map
Red-Breasted Nuthatch
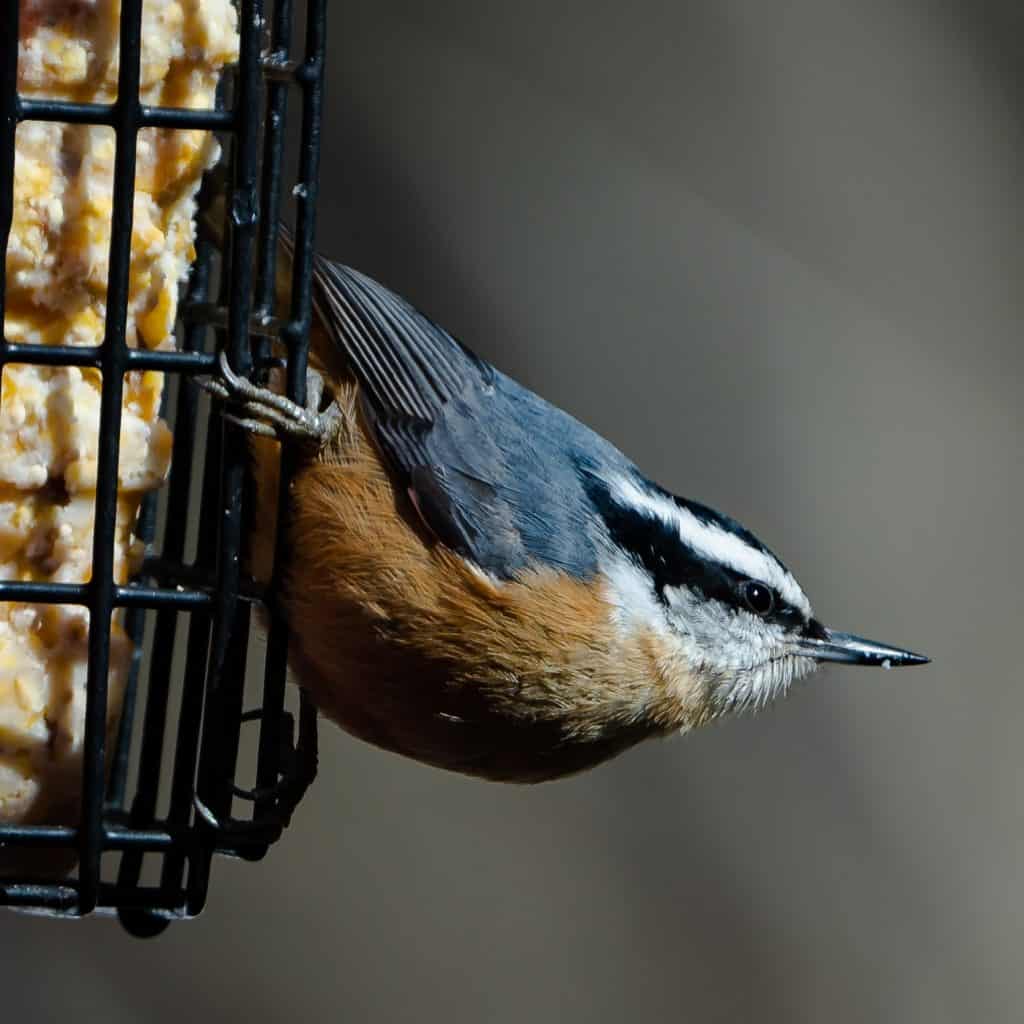

Appearance: The red-breasted nuthatch is a small bird about 4.5″ long, with gray/blue backs, a white head with black stripes running over either eye, orange-cinnamon-colored breast, and a pointy pick-like beak. The females look the same except their underside is a more faded color. Usually spotted climbing upside-down on a deciduous tree foraging for insects beneath the bark.
Diet: Insects, spiders, and other bugs.
Feeder food: Suet, sunflower seeds, shelled peanuts, fruit.
Habitat: Forested areas primarily comprised of coniferous trees (i.e. pines). Woodsy areas of deciduous trees in the east. Southern birds prefer mountainous regions until winter comes in which case they head to lower land.
Nesting: Red-breasted nuthatches are cavity nesters and they prefer to excavate their own holes. They have 1 brood/season, and 6 eggs/brood, eggs are white & speckled with red-brown.
Migration: Red-breasted nuthatches are partial migrators. While many remain in their year-round range, others migrate south for winter.
Year-round range: Southern Alaska, states in the western third of the US, northern Minnesota & Wisconsin, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and New England as well as all Canadian provinces except Nunavut.
Winter range: US states that are not part of the year-round range.
Range Map
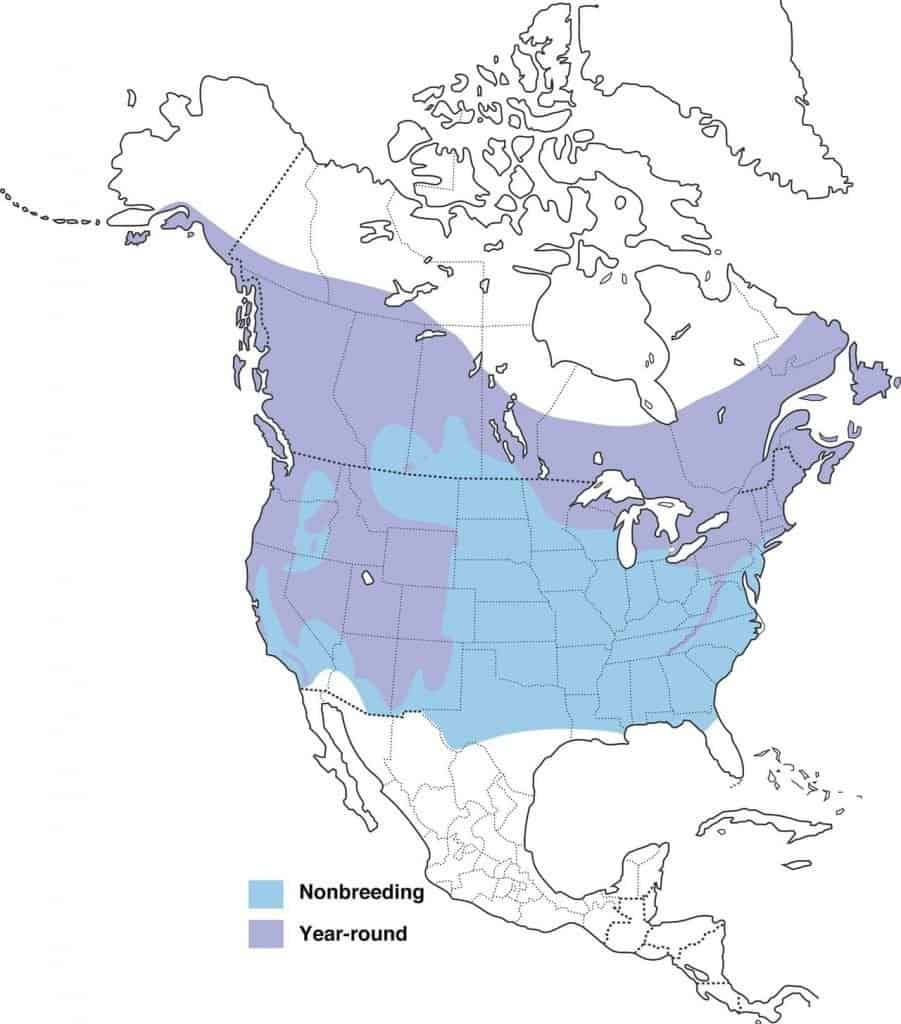
Rock Pigeon
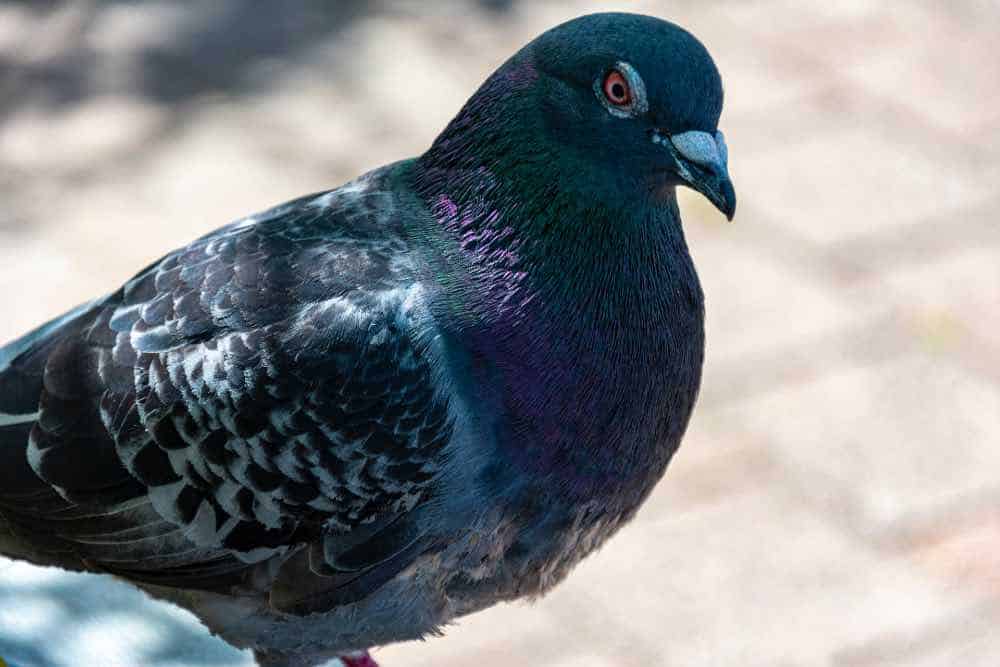

Appearance: Large bird 12-14″ long, chubby with blue/gray wings with black pointy tips, short red legs, black, round wide tail, and iridescent neck.
Diet: Grains, seeds, and fruit. Commonly seen scavenging trash cans for food.
Feeder food: Millet, cracked corn, black-oil sunflower seed, safflower, peanut hearts.
Habitat: Common around cities and towns as well as farmlands
Nesting: Rock pigeons build a large nest of sticks and grass wherever there’s a ledge (e.g. highway overpass, barns, bridges, tall buildings). 1-6 broods/year, 1-3 eggs/brood, eggs are white, incubation about 18 days and the young fledge at about 25-32 days.
Migration: Rock pigeons are not migrators. They remain in their year-round range all seasons of the year.
Year-round range: Every US state, the southernmost edges of Canada, and Mexico.
Range Map
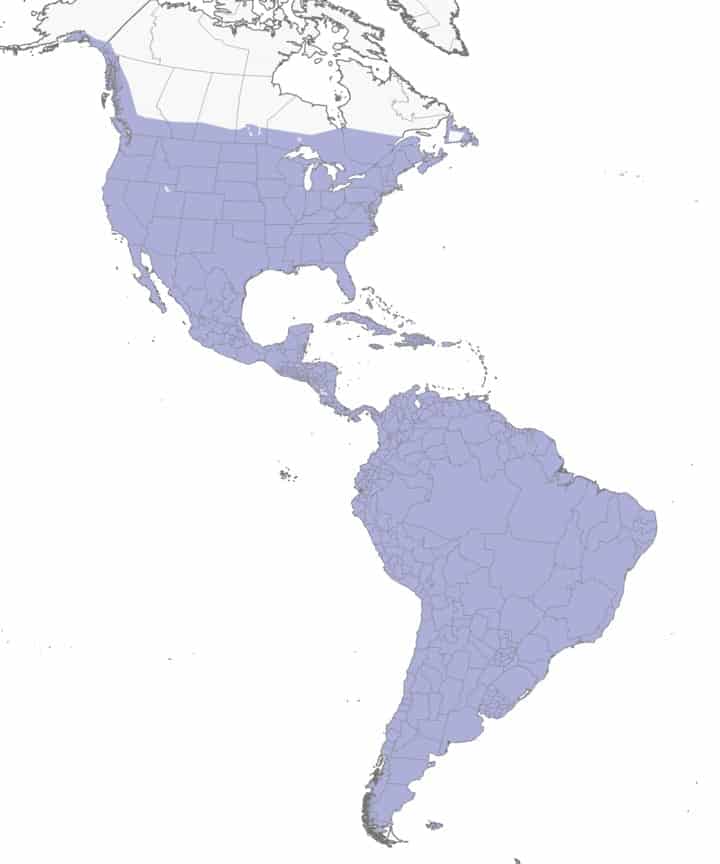
Tree Swallow
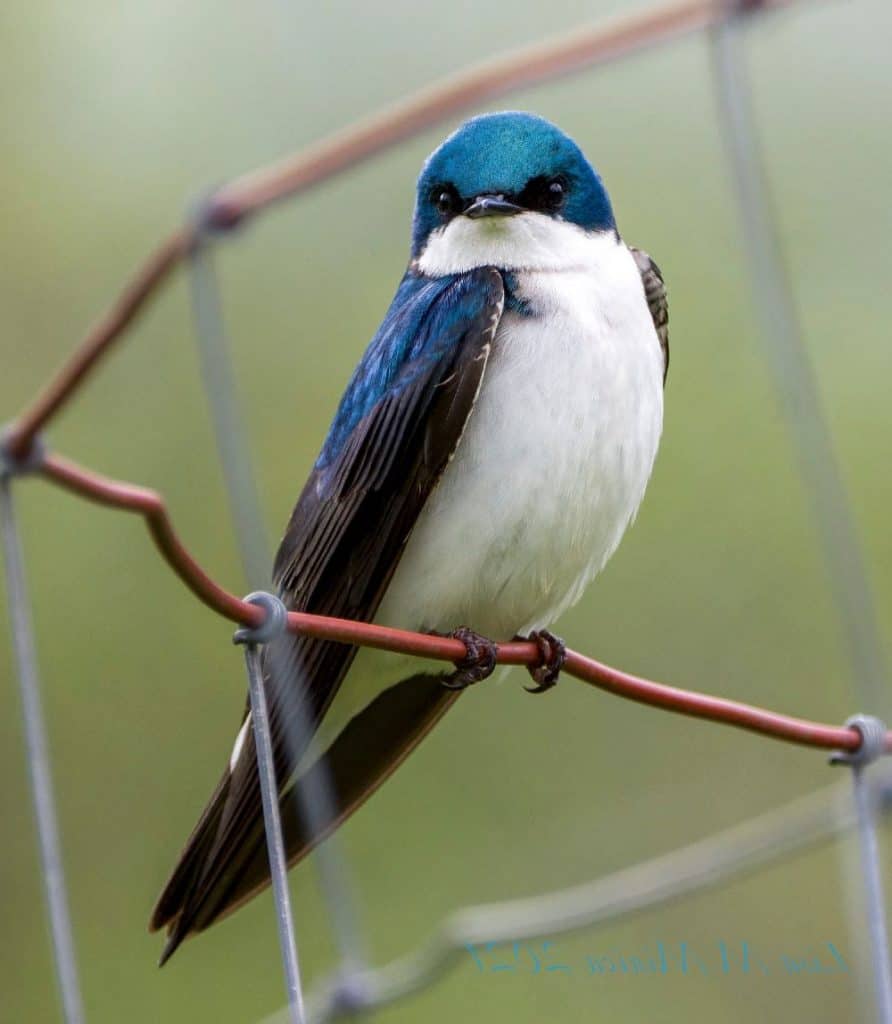

Appearance: 5-6″ long, dark metallic blue to blue/green with a white belly, notched tail, and pointed wing tips. Females have the same coloring but are a bit duller.
Diet: Insects and small fruits.
Feeder Food: Unlikely to visit a feeder.
Habitat: Open areas such as fields, large lawns, and marshes.
Nesting: Tree swallows are cavity nesters. They often take up residence in an old dead tree or existing hole left behind by other cavity nesters. They have 2-8 eggs, eggs are light pink then slowly fade to white. Incubation is 14-15 days and young fledge at about 18-22 days.
Range Map
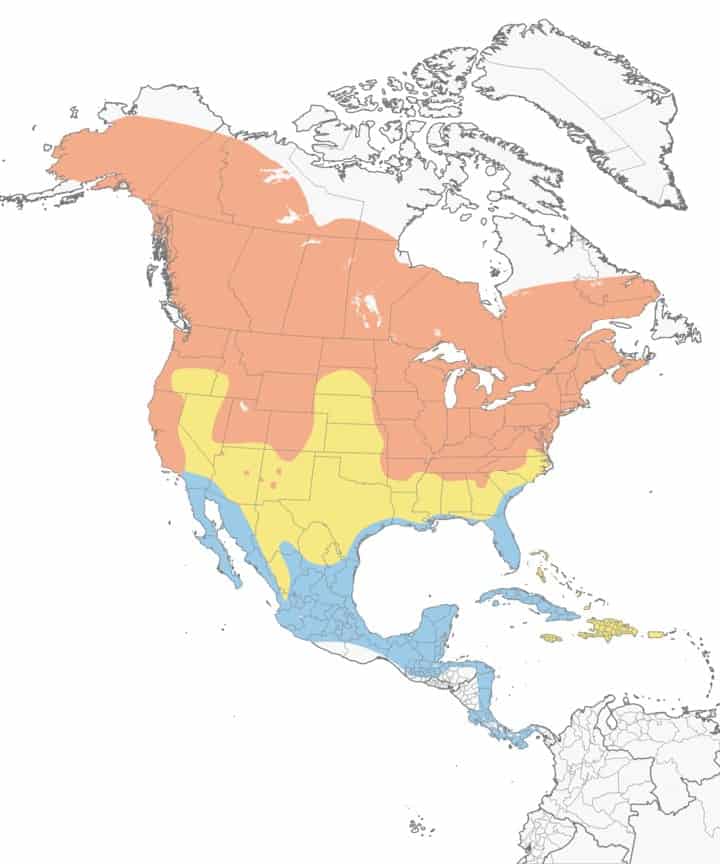
White-Breasted Nuthatch
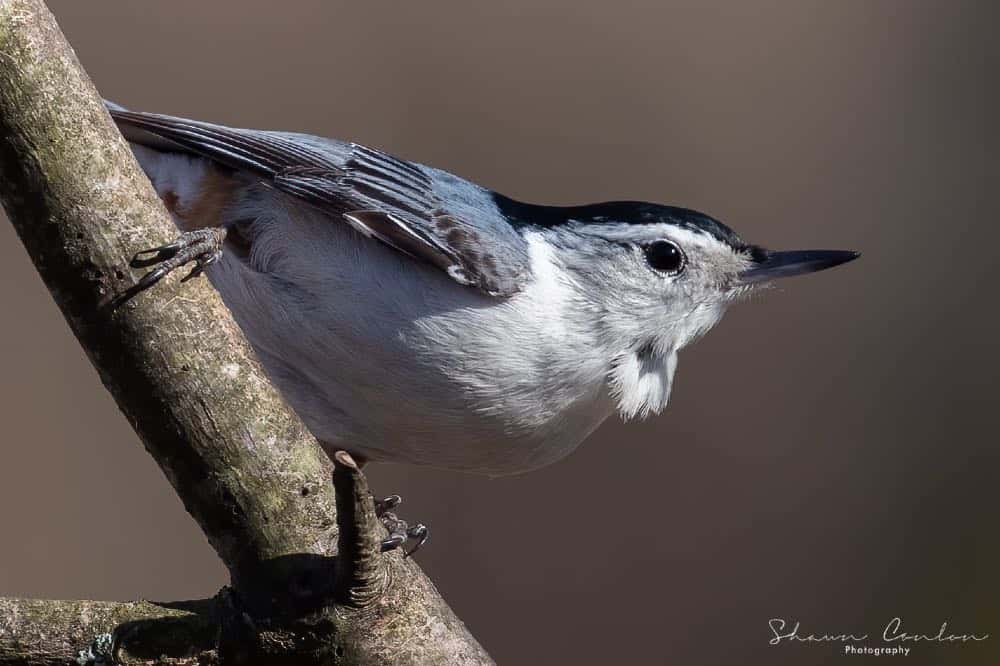

Appearance: 5-6″ long, gray/blue back, white head with a black cap, chestnut under the tail, and a long thin pick-like beak. Females look similar except their cap and neck are gray. Usually spotted climbing upside-down on a deciduous tree foraging for insects beneath the bark.
Diet: Insects & seeds.
Feeder food: Suet, sunflower seed, shelled peanuts.
Habitat: Near mature deciduous and mixed forests; wooded suburban areas such as orchards, parks, and backyards.
Nesting: White-breasted nuthatches are cavity nesters. They have 1 brood/season, 5-9 eggs/brood, eggs are white with brown markings, incubation is 11-12 days and young fledge at about 13-14 days.
Migration: White-breasted nuthatches are not migrators. They remain in their year-round range all seasons of the year. That said, a small part of the population may migrate to a strip in the southcentral US for the winter.
Year-round range: Every US state, Canada’s southern provinces, and Mexico.
Range Map
Conclusion
The great state of Nebraska hosts many different species of blue birds. Hopefully, you’ve identified the one you’re interested in within this article or just broadened your knowledge of blue birds in Nebraska. If you want to see more blue birds consider taking steps to attract them.


